
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Joint Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A direct prejudgement strategy that takes the diffraction ring as the analysis target is put forward to predict hot images induced by defects of tens of microns in the main amplifier section of high power laser systems. Analysis of hot-image formation process shows that the hot image can be precisely calculated with the extracted intensity oscillation of the diffraction ring on the front surface of the nonlinear plate. The gradient direction matching (GDM) method is adopted to detect diffraction rings. Recognition of simulated diffraction rings shows that it is feasible to directly prejudge hot images induced by those closely spaced defects and the defects that are far apart from each other. Image compression and cluster analysis are utilized to optimize the performance of the GDM method in recognizing actually collected diffraction images. Results show that hot images induced by defects of tens of microns can be directly prejudged without redundant information.
diffraction rings gradient direction matching method hot images intensity oscillation High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(3): 03000e52
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
It is rare for a conventional direct detection method to measure the transmittance uniformity of mirrors with rigorous standards, especially to meet the requirement of transmittance/reflectance and phase detection simultaneously. In this study, a new method of self-calibrated balanced heterodyne detection (SCBHD) is proposed. It can be self-calibrated by a two-channel structure to overcome the environmental effects in large optics scanning detection by employing highly accurate heterodyne interference. A typical transmittance measurement experiment was performed at 1053 nm wavelength via SCBHD. A standard deviation (SD) of 0.038% was achieved in the preliminary experiment. The experimental results prove to reduce the SD by approximately two orders of magnitude compared with the conventional direct detection method in the same condition. The proposed method was verified as being promising not only for its wider dynamic measurement range and its higher accuracy but also for its simultaneous transmittance and phase detection ability.
120.3940 Metrology 240.6700 Surfaces 300.6490 Spectroscopy, surface Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(6): 061201
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
表面微小疵病在用不同波长的光照明时,其光学图像会存在不同程度的非线性放大畸变现象,对成像信息中的目标提取和信噪比(SNR)将产生一定的影响。提出利用红、绿、蓝三基色光源辐照下的疵病图像进行动态彩色编码成像的方法,经像素级图像融合后可实现高冗余信息的图像合成,从而在获取表面微小疵病丰富细节的同时可进一步提高信噪比。分析了针对三基色图像进行彩色编码的理论,提出了基于图像梯度的动态权值融合成像方法,同时给出了光谱非线性放大信号的噪声分析模型,通过理论分析和数值模拟两方面,充分验证了动态权值融合降低标准偏差的有效性。在明场表面疵病成像实验中,采用三基色平衡响应的彩色互补金属氧化物半导体(CMOS)相机,分别获取了单个微米量级表面疵病点的三基色滤波图像,并通过与传统边缘提取、非动态权值组合等方法的结果比对,验证该优化方法可得到一幅细节更为丰富的高SNR图像。在暗场表面疵病成像实验中,以图像灰度平均梯度和提取到的疵病数量为评价参数,即从优化图像质量和疵病识别能力两个方面,进一步验证该优化在高保真和低噪声方面的有效性。提出的动态彩色编码融合成像方法可有效降低光谱非线性放大带来的噪声。
光学器件 表面疵病 动态彩色编码 高功率激光技术
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
比较了高通量密度下损伤点分别位于上游介质的前后表面时热像的位置及峰值光强的区别。讨论了热像交替排布的现象及峰值光强随损伤点尺寸的变化规律。针对上游光学元件中的损伤点是诱发后续光路中热像的主要因素, 提出了以损伤点经一定传输距离后引起的衍射环图像为分析对象的热像预判技术。该技术运用高信噪比的梯度方向匹配算法来获取衍射环图像的特征信息, 进而反演出衍射距离和损伤点尺寸。利用液晶空间光调制器产生的单个等效损伤点的衍射图像证明了该方法的有效性; 并采用光学元件上实际存在的损伤点所引起的衍射环图像分析了该算法反演多个损伤点时抑制噪声干扰的能力及其空间分辨率。
激光技术 高通量密度 损伤点 热像 衍射环 梯度方向匹配
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
为有效检测光学元件体内的缺陷情况, 利用全内反射技术, 让激光束在光学元件内部多次全内反射后获得缺陷的散射光斑图像, 结合基于最小二乘法的椭圆拟合等方法对散射图像进行处理, 得到缺陷的三维位置信息。对该方法进行了实验验证, 实验结果表明, 扫描采集35幅图像即可完成对尺寸为150 mm×120 mm×20 mm的大口径光学元件的全部缺陷检测, 待测样品缺陷点的深度位置定位精度优于150 μm, 说明该方法可以有效检测大口径光学元件缺陷点。针对可能影响实验结果的误差来源和限制系统分辨率的因素进行了分析, 结果表明提高成像系统横向分辨率或减小激光束横截面宽度均可有效地提高系统的分辨率。
测量 缺陷深度位置检测 全内反射 大口径光学元件 椭圆拟合 分辨率
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A universal phase mismatch compensation method, which can be applied to temperature-insensitive frequency conversion, is experimentally demonstrated. In this method, two nonlinear crystals and an electro-optic crystal are cascaded. The generated phase mismatch in the nonlinear crystal can be well compensated for in the electro-optic crystal, thereby improving the stability of frequency conversion. In the proof-of-principle experiment, temperature-insensitive second and third harmonic generation (SHG and THG) are investigated by cascading KH2PO4 (KDP) and KD2PO4 (DKDP) crystals. The experimental results show that the temperature acceptance bandwidths of SHG and THG are 2.1 and 2.3 times larger, respectively, than that of the traditional method employing a single crystal. Meanwhile, the effectiveness of this method is also analyzed at a high power density, and a solution for the case of a nonuniform temperature is also discussed. Furthermore, angle-insensitive SHG is demonstrated to prove that this method can significantly reduce the influence of various unfavorable factors on frequency conversion. The demonstrated method may have potentially important applications in the nonlinear optical frequency conversion system.
Nonlinear optics second and third harmonic generation (SHG and THG) cascaded nonlinear processes Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2016, 14(1): 6100308
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A compensation method for phase mismatch caused by temperature variation during the frequency conversion process is proposed and the theoretical model is established. The method is based on the principle that phase mismatch can be compensated via the electro-optic effect based on a compensation scheme consisting of two nonlinear crystals and an electro-optic crystal; further, a new dimension adjustment can be achieved by changing the voltage. In a proof-of-principle study, frequency conversion from 1053 nm to 526.5 nm and 351 nm by cascade KH2PO4 (KDP) and KD2PO4 (DKDP) crystals, respectively, is presented as an example. Three-dimensional numerical simulations are conducted to show that the conversion efficiency of frequency doubling and tripling varies with temperature. The results show that the temperature acceptance bandwidth of doubling and tripling can be 2.4 and 3.4 times larger, respectively, than that of the traditional method using a single crystal. We also analyze the stability of the conversion efficiency for 192 beams by our proposed method when the temperature is randomly varied within the range of 24°C–26°C. The standard deviation of the conversion efficiency of frequency doubling and tripling decreases from 1.25% and 6.61% to 0.18% and 0.56%, respectively. In addition, the influence of the reflection loss on the output efficiencies is also analyzed and the results show that it is very small. This indicates that this method may be effective in reducing the temperature sensitivity of conversion efficiency.
Lasers frequency doubled Harmonic generation and mixing Nonlinear wave mixing. Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2016, 14(1): 525
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 德国马普天文所, Knigstuhl 17, D-69117 Heidelberg, 德国
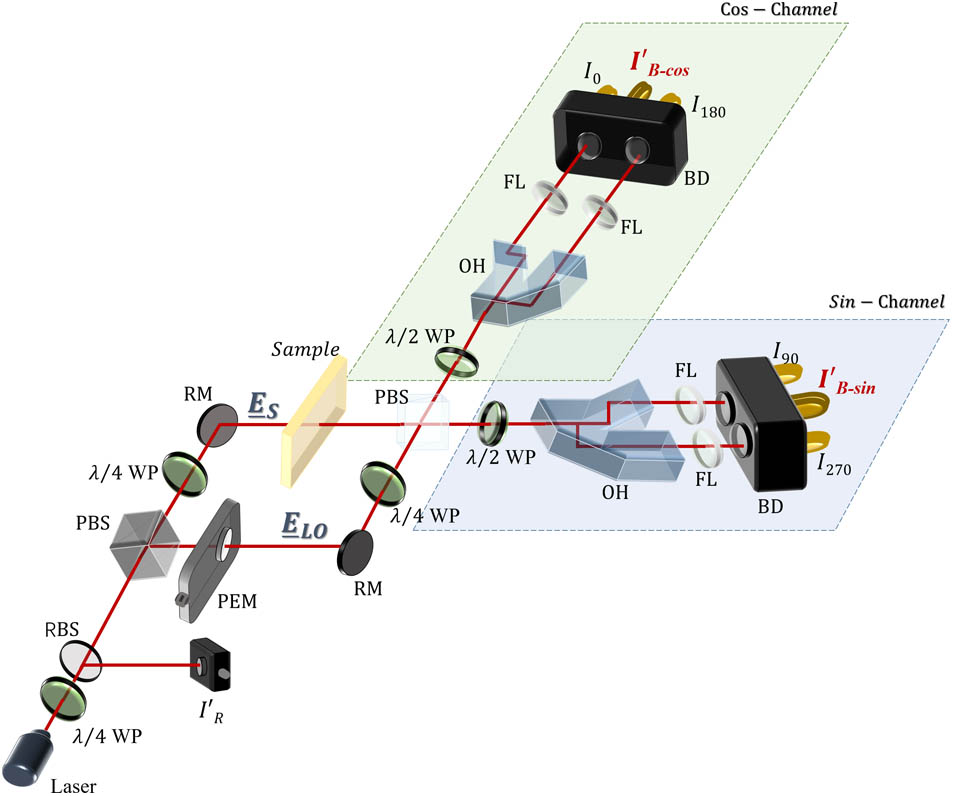
This paper describes the development of a novel infrared point-diffraction interferometer (IPDI), which can be readily applied to real-time quantitative phase measurement. We generate reference wave with the help of Michelson-like unit combined with a low-pass spatial filter, and extract the phase information using windowed Fourier transform algorithm from single off-axis fringes. The arrangement of the proposed setup offers a quasi-common-path geometry, which could significantly minimize the systematic errors. The proposed method of IPDI is effective and sufficient for the dynamic process measurement of small deformation with higher spatial resolution compared with the conventional off-axis scheme. The feasibility of the proposed setup is demonstrated, followed by methods of reconstruction and system calibration. The nanoscale repeatability is achieved in our experiment.
测量 点衍射干涉仪 分束器 离轴 窗口傅里叶变换 measurement point-diffraction interferometer beam splitter off-axis windowed Fourier transform Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2013, 11(1): 0508001
1 国家测绘地理信息局第一航测遥感院, 陕西 西安710054
2 南京森林警察学院, 江苏 南京210046
3 北京林业大学测绘与3S技术中心, 北京100083
4 北京林业大学生态研究中心, 北京100083
多光谱遥感数据蕴含着大量的地表立地信息, 而传统立地质量评价体系主要使用了人工地面调查数据。 为了建立一套有效的立地质量评价体系, 以内蒙古赤峰市旺业甸林场为研究对象, 基于研究区域的多光谱遥感数据结合地面小班调查数据, 采用一种改进的反向传播人工神经网络(back Propagation artificial neural network, BPANN)模型, 以落叶松为例, 建立了遥感光谱因子结合立地因子与地位指数关系的神经网络模型, 对研究区域的小班进行立地质量评价研究。 通过训练数据集的敏感度分析剔除弱相关或不相关的因子, 简化了神经网络的规模, 提高了网络的训练效率, 得到了最优的地位指数预测模型, 模型的预测精度达到95.36%, 与使用传统小班调查数据建立的神经网络模型的预测结果进行了比较, 精度提高了9.83%, 说明使用多光谱遥感数据+小班调查数据确定的落叶松地位指数预测模型具有最高的预测精度。 多光谱遥感数据十分适用于森林立地质量评价, 改进BP神经网络具有理想的预测精度, 充分证实了该方法的有效性和优越性。
立地质量 多光谱遥感 神经网络 Site quality Multispectral remote sensing Neural Network 光谱学与光谱分析
2013, 33(10): 2815
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 德国马普天文所, Knigstuhl 17, D-69117 Heidelberg, 德国
介绍了一种结构简单紧凑、可用于高精度实时相位波前测量的红外点衍射干涉仪,采用类迈克耳孙的光学结构,并结合低通小孔滤波,同时使用窗口傅里叶变换的方法解调单幅离轴载波条纹。与传统波前测量技术相比,所提出的准共光路的光学系统结构有效地抑制了系统像差及外部环境干扰等对测量结果的影响,实现高精度和高分辨率的波前探测。实验结果表明,该方法能够实现高精度的相位测量,且其重复精度达到了纳米量级。
测量 点衍射干涉仪 分束器 离轴 窗口傅里叶变换





